Health insurance is essential for self-employed individuals. It can be costly, though.
But how much does it really cost? Being self-employed comes with many perks, like flexibility and independence. Yet, it also brings challenges, such as finding affordable health insurance. Without employer-provided options, self-employed people must navigate the market on their own.
This can be confusing and expensive. Understanding the costs involved is crucial to making informed decisions. In this blog post, we will explore the various factors that affect health insurance costs for self-employed individuals. We will also provide tips on finding the best coverage for your needs and budget. Stay tuned to learn more about navigating health insurance as a self-employed professional.
Introduction To Health Insurance For Self-employed
Choosing health insurance as a self-employed individual can be daunting. Unlike traditional employees, the self-employed must navigate this terrain alone. Understanding the costs and benefits is crucial. This section covers why health insurance matters, and the challenges faced.
Why It Matters
Health insurance is essential for everyone. For the self-employed, it provides financial security. Medical emergencies can be expensive. Without insurance, these costs can be overwhelming. Health insurance ensures that you get the care you need without financial strain.
Self-employed individuals often have unpredictable incomes. Health insurance can stabilize out-of-pocket healthcare costs. This helps in budgeting and financial planning.
Challenges Faced
Self-employed people face unique challenges in obtaining health insurance. One of the main challenges is cost. Without an employer to share the expense, premiums can be high. This can make it difficult to find affordable coverage.
Another challenge is the complexity of choices. There are many plans available, each with different benefits and costs. Navigating these options requires time and research. This can be stressful for those who are already managing their own business.
A lack of information can also be a hurdle. Many self-employed individuals may not know what plans exist or how to choose the right one. This can lead to inadequate coverage or higher costs.
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| High Premiums | Increased financial burden |
| Complex Choices | Time-consuming research |
| Lack of Information | Poor coverage choices |
Understanding these challenges can help in finding better solutions. Awareness is the first step toward securing the right health insurance.
Types Of Health Insurance Plans
As a self-employed individual, understanding the different types of health insurance plans is crucial. Choosing the right plan can help manage costs while ensuring you get the coverage you need. Let’s break down the types of health insurance plans available to you.
Individual Plans
Individual plans are designed for those who need coverage for themselves only. These plans offer various levels of coverage, from basic to comprehensive. Here are some key features of individual plans:
- Coverage for routine check-ups and preventive care
- Options for specialist visits and hospital stays
- Prescription drug coverage
Individual plans can be tailored to fit your specific health needs and budget. Premiums and deductibles vary based on the level of coverage you choose.
Family Plans
Family plans provide coverage for you and your dependents. These plans typically offer a more cost-effective way to ensure the entire family is covered. Key features include:
- Coverage for all family members under one plan
- Preventive care and routine check-ups for children and adults
- Maternity and pediatric care
Family plans can be a great option if you have children or other dependents. The premiums and out-of-pocket costs are often shared among family members.
Short-term Plans
Short-term plans are temporary solutions for those between jobs or waiting for other coverage to begin. These plans generally offer:
- Basic coverage for unexpected illnesses or injuries
- Lower premiums compared to long-term plans
- Flexible coverage periods, typically up to 12 months
Short-term plans are not meant for long-term coverage. They often exclude pre-existing conditions and comprehensive care.
Understanding these types of health insurance plans helps you make informed decisions about your healthcare needs. Choose a plan that fits your lifestyle and budget.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
Understanding the factors influencing health insurance costs can help self-employed individuals make informed decisions. Several elements play a role in determining the cost of health insurance. This section will cover the main factors affecting these costs, including age and health, location, and coverage level.
Age And Health
Your age and overall health significantly impact health insurance costs. Generally, older individuals pay higher premiums. This is because they are more likely to need medical care. On the other hand, younger and healthier individuals usually pay lower premiums. Insurance companies assess your medical history, current health conditions, and lifestyle choices. Factors like smoking, chronic diseases, and past medical treatments can raise costs.
Location
The location where you live also affects health insurance costs. Different states and regions have varying healthcare costs. Urban areas may have higher premiums due to increased access to healthcare facilities. Conversely, rural areas might have lower premiums. State regulations and local healthcare policies can influence costs too. For instance, states with more healthcare mandates might have higher premiums.
Coverage Level
The coverage level you choose directly impacts your health insurance costs. Plans with more comprehensive coverage usually come with higher premiums. These plans often include lower deductibles and broader networks of healthcare providers. Conversely, plans with minimal coverage have lower premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs. It’s crucial to balance your healthcare needs with your budget when selecting a plan.
| Factor | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|
| Age and Health | Older age and poor health increase costs |
| Location | Urban areas and states with more mandates often have higher costs |
| Coverage Level | More comprehensive plans have higher premiums |
By understanding these factors, self-employed individuals can better navigate the complexities of health insurance costs. Consider each element carefully to make the best decision for your situation.
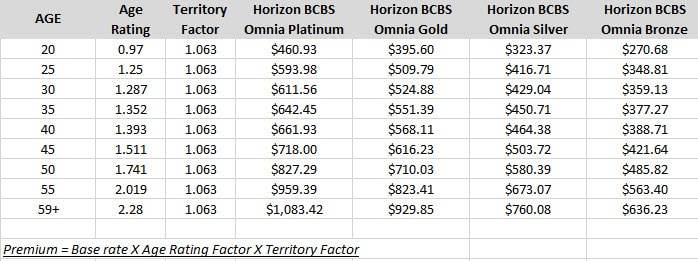
Credit: www.newjerseyinsuranceplans.com
Comparing Different Health Insurance Providers
As a self-employed individual, finding the right health insurance provider is crucial. Each provider offers different plans, benefits, and costs. To make an informed decision, it is essential to compare these providers.
Top Providers
Here are some of the top health insurance providers for self-employed individuals:
- Blue Cross Blue Shield
- UnitedHealthcare
- Kaiser Permanente
- Aetna
- Cigna
Key Differences
Each provider has unique offerings. Here’s a comparison:
| Provider | Plan Types | Monthly Premium | Deductibles | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blue Cross Blue Shield | HMO, PPO | $300 – $600 | $1,000 – $3,000 | Comprehensive |
| UnitedHealthcare | PPO, HMO, EPO | $250 – $700 | $1,500 – $4,000 | Extensive |
| Kaiser Permanente | HMO | $200 – $550 | $1,000 – $2,500 | Integrated |
| Aetna | PPO, HMO, EPO | $275 – $650 | $1,500 – $3,500 | Broad |
| Cigna | PPO, HMO | $300 – $600 | $1,000 – $3,000 | Wide |
Customer Reviews
Customer feedback is important for evaluating providers. Here are some highlights:
- Blue Cross Blue Shield: Reliable, but higher premiums.
- UnitedHealthcare: Good network, but costly deductibles.
- Kaiser Permanente: Great integrated care, limited to certain areas.
- Aetna: Broad coverage, but customer service needs improvement.
- Cigna: Comprehensive, but higher out-of-pocket costs.
Estimating Monthly Premiums
Estimating monthly premiums for health insurance is crucial for self-employed individuals. Knowing the average costs and using cost calculators can help you budget effectively. Real-life examples also provide a clear picture of what to expect.
Average Costs
The average cost of health insurance varies. On average, self-employed individuals can expect to pay between $200 and $600 per month for individual plans. For family plans, the cost ranges from $700 to $1,600 per month. Factors like age, location, and coverage level affect these amounts.
Cost Calculators
Online cost calculators are valuable tools for estimating monthly premiums. Websites like Healthcare.gov and private insurance companies offer these tools. Simply input your details like age, income, and family size. The calculator will provide a range of premium estimates. Here’s a quick overview of how to use them:
- Enter your age and location.
- Select your coverage level (bronze, silver, gold, or platinum).
- Include any dependents.
- Review the estimated premium cost.
Real-life Examples
Let’s look at some real-life examples. Consider a self-employed graphic designer in California:
- Individual Plan: $450 per month
- Family Plan: $1,200 per month
Or, a freelance writer in Texas:
- Individual Plan: $350 per month
- Family Plan: $1,000 per month
These examples illustrate the variation in costs based on location and profession.
Tax Deductions And Credits
Understanding tax deductions and credits can help reduce your health insurance costs. If you’re self-employed, you may qualify for some beneficial tax breaks.
Self-employed Health Insurance Deduction
The Self-Employed Health Insurance Deduction allows you to deduct health insurance premiums. This includes premiums for yourself, your spouse, and your dependents. You can claim this deduction on your federal income tax return. It reduces your adjusted gross income, resulting in lower overall taxes.
Here are the basic eligibility requirements:
- You must be self-employed.
- You must not be eligible for employer-sponsored health insurance.
- You must pay the premiums yourself.
For example, if you pay $5,000 in premiums, you can deduct this amount. This deduction can significantly lower your taxable income.
Premium Tax Credits
Premium Tax Credits help lower your monthly insurance payments. They are available to those purchasing insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace. The amount of the credit depends on your income and household size.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Income Level | Credit Amount |
|---|---|
| 100%-400% of Federal Poverty Level (FPL) | Eligible for tax credits |
| Above 400% of FPL | Not eligible |
To apply for these credits, you must enroll in a plan through the Marketplace. The credits can be applied directly to your monthly premiums. This reduces the amount you need to pay out-of-pocket each month.
Consider these options to save on health insurance costs. Both deductions and credits can provide significant financial relief.
Additional Costs To Consider
When you’re self-employed, health insurance costs can be a significant concern. Beyond the premium, there are additional costs you must consider. These can affect your overall healthcare budget. Here, we will break down the additional costs you need to be aware of.
Co-payments
Co-payments, or co-pays, are fixed amounts you pay for specific healthcare services. You pay these fees each time you get a service. For example, you might pay $20 for a doctor visit or $10 for a prescription. These co-pays vary by plan and service type. Always check your plan details to know your co-pay amounts.
Deductibles
Deductibles are amounts you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance starts covering costs. If your deductible is $1,000, you must pay $1,000 in medical expenses first. After that, your insurance covers a portion of the costs. High deductible plans generally have lower premiums, but you pay more upfront. Consider your healthcare needs when choosing a deductible amount.
Out-of-pocket Maximums
The out-of-pocket maximum is the most you will pay in a year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance covers 100% of your costs for the rest of the year. This includes co-pays, deductibles, and coinsurance. Knowing this number helps you plan for worst-case scenarios. It provides a safety net for high medical expenses.
| Cost Type | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Co-Payments | Fixed fees for specific services | $20 per doctor visit |
| Deductibles | Amount paid before insurance starts | $1,000 per year |
| Out-of-Pocket Maximums | Max amount paid in a year | $5,000 per year |
Understanding these additional costs helps you budget better. It ensures you are prepared for any medical expenses. Always read the details of your insurance plan carefully. This helps you make informed decisions and avoid unexpected costs.
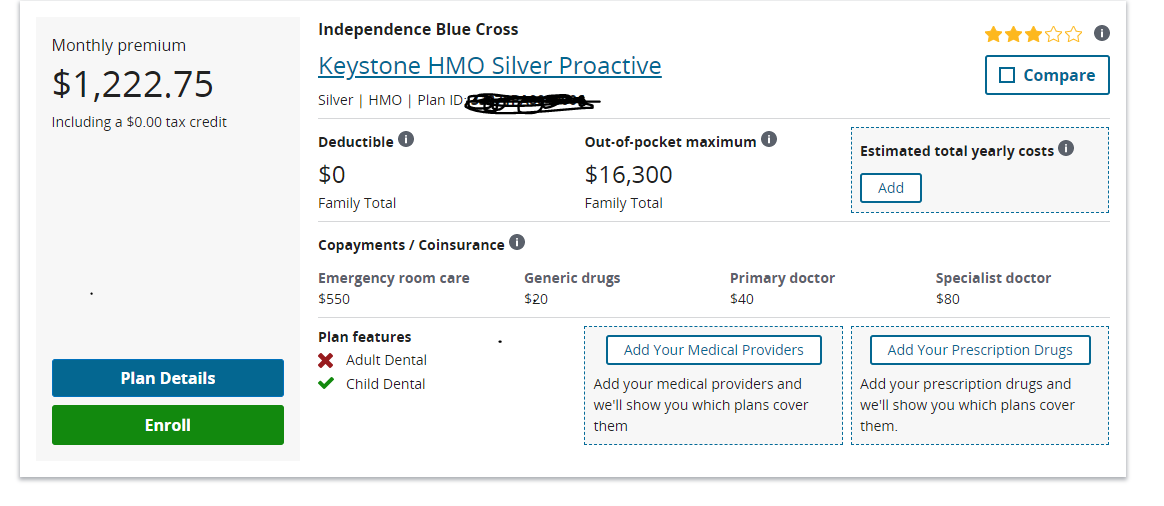
Credit: accordingtotrish.com
Tips For Reducing Health Insurance Costs
Health insurance costs can be overwhelming for the self-employed. Finding ways to reduce these costs is essential. Here are some practical tips to help you lower your health insurance expenses.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact your health insurance premiums. Insurance companies often offer discounts for those who demonstrate healthy habits. Here are some tips:
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can reduce medical issues.
- Eat Healthily: A balanced diet helps maintain overall health.
- Quit Smoking: Non-smokers usually get lower premiums.
- Limit Alcohol: Reduced alcohol intake can lower health risks.
Using A Broker
A health insurance broker can help you find the best deals. Brokers have access to multiple insurance plans and can help you compare options. Benefits include:
- Expert Advice: Brokers understand the market and can guide you.
- Time-Saving: They do the research, saving you time and effort.
- Cost-Efficiency: Brokers can often find more affordable plans.
Exploring Alternative Options
Consider alternative health insurance options to reduce costs. Some alternatives include:
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): These accounts offer tax advantages.
- Short-Term Health Insurance: Temporary coverage at a lower cost.
- Health Care Sharing Ministries: Members share medical expenses.
- Catastrophic Health Insurance: Low premiums, covering major expenses.
Evaluate these options to find one that fits your needs and budget.

Credit: www.ramseysolutions.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Does Health Insurance Cost For Self-employed Individuals?
Health insurance costs for self-employed individuals vary widely. Factors include location, age, and coverage level. On average, expect to pay between $300 and $600 monthly for a decent plan. Shopping around and comparing different providers can help you find the best deal.
What Factors Influence Self-employed Health Insurance Costs?
Several factors influence health insurance costs for self-employed individuals. These include age, location, health status, and the type of coverage chosen. Additional factors may include smoking status and family size. Understanding these factors can help you estimate your potential costs more accurately.
Are There Tax Benefits For Self-employed Health Insurance?
Yes, self-employed individuals may qualify for tax deductions on health insurance premiums. The IRS allows deductions for premiums paid for yourself, your spouse, and dependents. This deduction can significantly reduce your taxable income and overall tax burden.
Can Self-employed Individuals Get Subsidies For Health Insurance?
Self-employed individuals may qualify for health insurance subsidies through the Health Insurance Marketplace. Eligibility depends on your household income and size. These subsidies can lower your monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs, making health insurance more affordable.
Conclusion
Understanding health insurance costs for self-employed individuals is crucial. It impacts your budget and well-being. Researching options can save money. Choose plans fitting your needs and finances. Consult a professional if confused. Stay informed and protect yourself. Investing in the right health insurance pays off.
Remember, your health is your wealth.
You might be interested in learning more about the different types of health insurance policies available for self-employed individuals. Speaking of health insurance, you might want to check out the Wikipedia article on Health Insurance for an overview of how it works. Additionally, understanding the Affordable Care Act can also be beneficial, so I recommend reading the Wikipedia page on the Affordable Care Act. This legislation plays a significant role in the health insurance landscape for the self-employed. And if you’re curious about tax implications, the Wikipedia article on Tax Deductions will provide you with great insights on how to potentially save on your health insurance premiums. All these resources can help empower you to make informed decisions as you navigate the complexities of health insurance.